Fibroadenoma: A Solid Lump In Breast

A benign (noncancerous) breast bulge is called a fibroadenoma. These firm, spherical, and smooth tumors are made up of a mass of glandular and fibrous tissue. Breast cancer can occasionally be discovered in conjunction with a fibroadenoma, but this is extremely uncommon.
How common are fibroadenomas?
The majority of breast lumps are benign, including fibroadenomas. A fibroadenoma is the most frequent type of benign breast mass.
What are the types of fibroadenomas?
A range of modifications to the tissue supporting the breast include fibroadenomas. The majority of fibroadenomas are straightforward. The risk of breast cancer is not often elevated by these tumors. This range of breast changes include complex fibroadenomas, fibroepithelial lesions, and benign phyllodes tumors. It’s necessary to remove these masses.
What causes fibroadenomas?
Physicians are unsure of the causes of certain patients’ fibroadenomas. They can increase during pregnancy and lactation and then shrink again later, and younger women are more likely to have them.
What are the signs and symptoms of fibroadenomas?
Fibroadenomas are typically 2 to 3 cm smooth, slippery, movable masses that can either disappear on their own, remain the same, or develop in size. They are surgically removed if they grow larger, become painful, or alter and take on a concerning appearance.
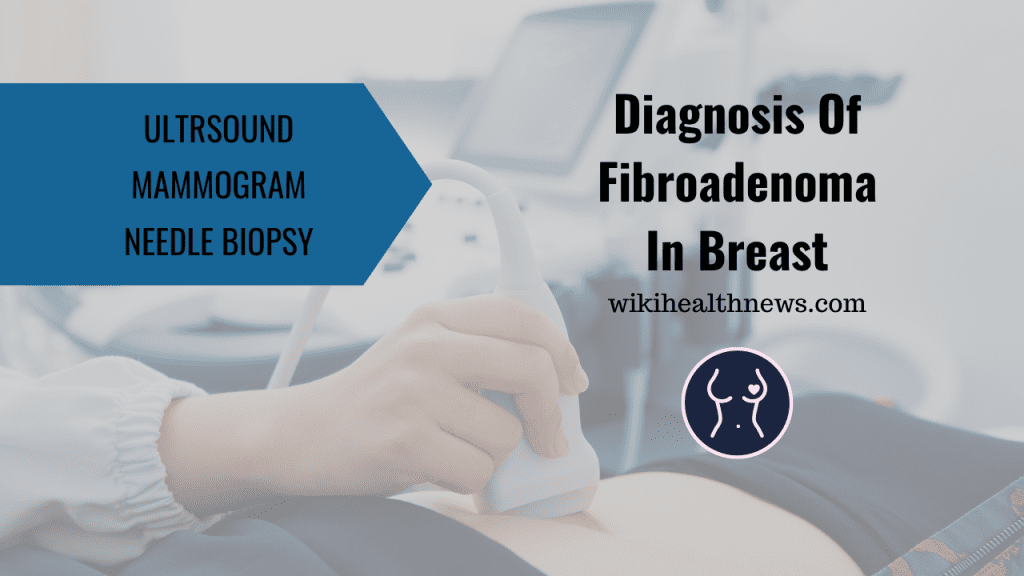
How is a fibroadenoma diagnosed?
Anytime you see a breast lump or other breast changes, contact your healthcare professional. Some fibroadenomas are inconspicuously small. These tests may be done by your doctor to identify a fibroadenoma if you or your healthcare provider discover a lump:
- Ultrasound and/or mammography imaging scans.
- Core needle breast biopsy with image guidance.
How are fibroadenomas managed or treated?
Some fibroadenomas reduce in size or go away on their own. Your doctor might advise that you undergo clinical examinations and possibly ultrasounds every six months for the following two years to ensure the fibroadenoma doesn’t change if a biopsy reveals the lump isn’t cancerous.
Do fibroadenomas need to be removed?
Not all fibroadenoma tumors need removal, small ones can be left alone. If it shows signs of rapid growth, pain or becomes hard it will need removal. Most of the removal surgery for fibroadenoma breast is done due to cosmetic reasons or scare of cancer. After a woman attains menopause these tumors are likely to shrink.
What is the cost of surgery for fibroadenoma breast?
It depends on the number of lumps, their size and involvement of one side or both breasts. This surgery is done under general anesthesia. It will require a skilled surgeon to avoid any cosmetic harm. Usually this surgery costs around 55,000 to 70,000 rupees depending on the infrastructure and service quality of the hospital.
How can I prevent fibroadenomas?
Unfortunately, there is nothing you can do to reduce your risk of developing fibroadenomas. To lessen your risk of developing breast cancer and to find it when it’s most treatable, follow these recommendations:
- Drink in moderation.
- Self-examinations of breast
- Regularly have mammograms done.
- Make wise food decisions, exercise, and keep your weight in check.
When should I visit a doctor?
Breast discomfort or alterations (development in the fibroadenoma).
- Freshly detected breast lump.
- Nipple discharge or rash.
Can fibroadenomas turn into cancer?
When you feel a lump in the breast the immediate question comes into the mind is it a serious condition or a cancer. Really fibroadenoma in the breast are not so serious as they scare you. Turning into cancer is a rare event. However you will need to keep a watch on its growth and have a half yearly check with your doctor.
What happens if fibroadenoma is left untreated?
Most cases are left untreated under supervision. You will need a regular check to find out any increase in size. Usual course of these tumors is regression after menopause since they depend on estrogen hormone. Rapidly increasing size is alarming and needs biopsy. Any change in color of overlying skin, temperature, consistency or size should be reported to health care providers.