Urinary Incontinence: Not A Part Of Aging
Urinary incontinence is the loss of bladder control which is common and often an embarrassing problem. The initial problem stars with occasional leaks of urine during cough or sneeze. Subsequently, it progresses to having an urge to urinate that’s so sudden and strong you don’t get to a toilet in time.
Though it will be more often as people get older, urinary incontinence isn’t an inevitable consequence of aging. If it affects the daily activities, don’t hesitate to consult with doctors. For many people the simple lifestyle and dietary changes or medical care can treat this condition.
Symptoms of urinary incontinence:
Many people experience the occasional minor leaks of urine. Whereas, few may lose small to moderate amounts of urine more frequently.
Types of urinary incontinence include:
Stress incontinence:
Urine leaks when you exert pressure on the bladder. It may come from coughing, sneezing, laughing, exercising, or lifting something heavy.
Urge incontinence:
Have a sudden, intense urge to urinate continued by an involuntary loss of urine. You may have to urinate often, including throughout the night. Urge incontinence may be caused by a minor condition, such as infection, or more severe condition such as neurological disorder or diabetes.
Overflow incontinence:
They experienced frequent or constant dribbling of urine due to a bladder that doesn’t empty completely.
Functional incontinence:
A physical or mental impairment keeps you from the urge to the toilet in time. For example if you have severe arthritis, they may not be able to unbutton the pants quickly enough.
Mixed incontinence:
They will have more than one type of problems, most often this refers to a combination of stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
Causes:
Bladder leaks can be developed by everyday habits, followed by medical conditions or physical problems. A thorough evaluation by a doctor can help determine what’s behind your incontinence.
Certain drinks, foods and medications may act as diuretics which stimulate the bladder and increase the volume of urine. They include:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Carbonated drinks and sparkling water
- Artificial sweeteners
- Chocolate
- Chili peppers
- Foods those are high in spice, sugar or acid, especially citrus fruits
- Heart problems and BP medications, sedatives and muscle relaxants
- Large dose of vitamin C
Urinary incontinence may also develop by an easily treatable medical condition, such as:
Urinary tract infection: infection can irritate the bladder which will cause the strong urges to urinate and sometimes, incontinence.
Constipation: the rectum is located near to the bladder and shares many of the same nerves. Hard, impacted stool in rectum causes these nerves to be overactive and increase urinary frequency.
Persistent urinary incontinence:
Urinary incontinence can also be a persistent condition developed by underlying physical problems or changes including:
Pregnancy: hormonal changes and the more weight of the fetus can lead to stress incontinence.
Childbirth: vaginal delivery can weaken muscles needed for bladder control and damage bladder nerve and supportive tissues, leading to a dropped pelvic floor. With prolapse the bladder, uterus, rectum or small intestine can be pushed down from the usual position and protrude into the vagina. Such protrusion may be associated with incontinence
Changes with age: aging of the bladder muscle can decrease the bladder capacity to store urine. Also involuntary bladder contractions will take more time as you get older.
Menopause: After menopause women secrete less estrogen, a hormone that helps keep the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. Deterioration of that will aggravate incontinence.
Enlarged prostate: mostly in older men, incontinence often stems from enlargement of the prostate gland, a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Prostate cancer: In men stress incontinence or urge incontinence can be linked with treatment prostate cancer. But more often, incontinence is a side effect of the treatment for prostate cancer.
Obstruction: a tumor anywhere along the urinary tract can block the normal flow of urine, leading to overflow incontinence. Urinary stones are hard, stone-like masses that form in the bladder where sometimes cause urine leakage.
Neurological disorders: Multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, brain tumor or a spinal injury can interfere with nerve signals involved in bladder control and cause bladder weakness.
Risk factors:
Gender: Mostly women will have stress incontinence. Pregnancy, childbirth, menopause and normal female anatomy account for this difference. However, men who have prostate gland disease are at higher risk of urge and overflow incontinence.
Age: The older the muscle in the bladder and urethra, they lose some of their strength. Changes with age reduce how much of the bladder can hold and increase the chances of involuntary urine release.
Being overweight: Extra weight increases the pressure on the bladder and surrounding muscles which weaken them and allows the urine to leak out when coughing or sneezing.
Smoking: Tobacco use may increase the risk of leaks from the bladder.
Family history: If a close family member has incontinence of urine especially urge incontinence the risk of developing the condition is higher.
Some diseases: Neurological disease or diabetes may increase the risk of leakage.
Complication:
Complication of chronic problem includes:
- Skin problems: rashes, skin infections and sores can cause from constantly wet skin.
- Urinary tract infection: Incontinence can affect social work and personal relationships.
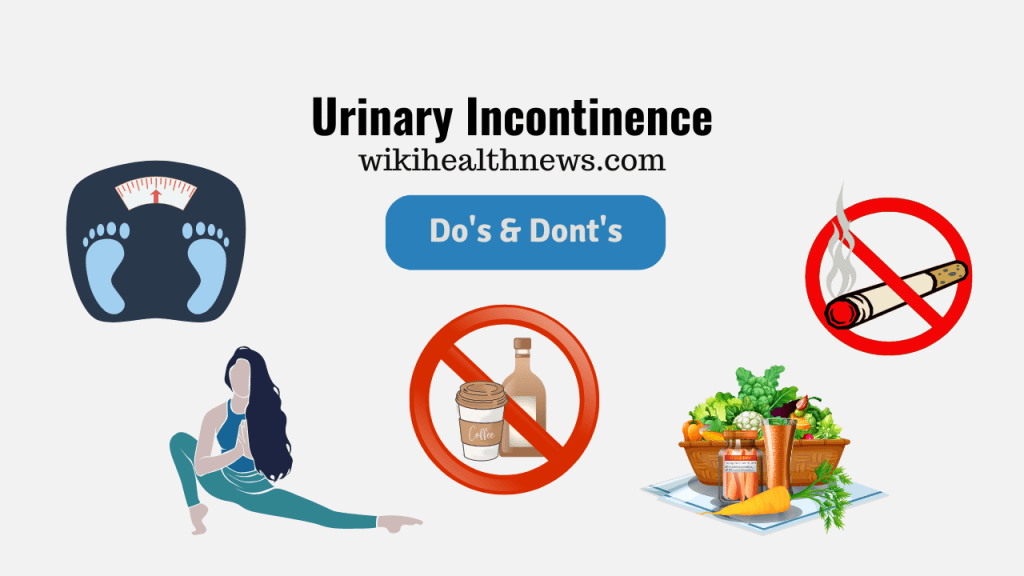
Prevention:
Leakage from bladder isn’t always preventable. However, to help decrease the risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Practice pelvic floor exercises
- Avoid bladder irritants, such as caffeine, alcohol and acidic foods.
- Eat more fiber which can prevent constipation, a cause of urinary incontinence
- Avoid smoking.
Read More